Pompei, Herculaneum & Villa Oplontis
|
By Dion Protani
|
Latest update: 9 January 2024
|
|
The Archaeological areas of Pompei, Herculaneum and Torre Annunziata has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1997.
The listing relates to three archaeological sites that lie in the shadow of Mount Vesuvius on the outskirts of Naples. Pompeii, Herculaneum and Villa Oplontis in Torre Annunziata offer a fascinating glimpse into life in these Ancient Roman towns. |
Related links
Profile
The Archaeological Areas of Pompei, Herculaneum, and Torre Annunziata form a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the Campania region of southern Italy.
This site includes the ancient Roman cities of Pompei and Herculaneum, both famously destroyed by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, as well as the ruins of the Roman villa at Torre Annunziata. Together, these archaeological areas offer a fascinating glimpse into the daily life and culture of the ancient Roman civilization.
This site includes the ancient Roman cities of Pompei and Herculaneum, both famously destroyed by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, as well as the ruins of the Roman villa at Torre Annunziata. Together, these archaeological areas offer a fascinating glimpse into the daily life and culture of the ancient Roman civilization.
History
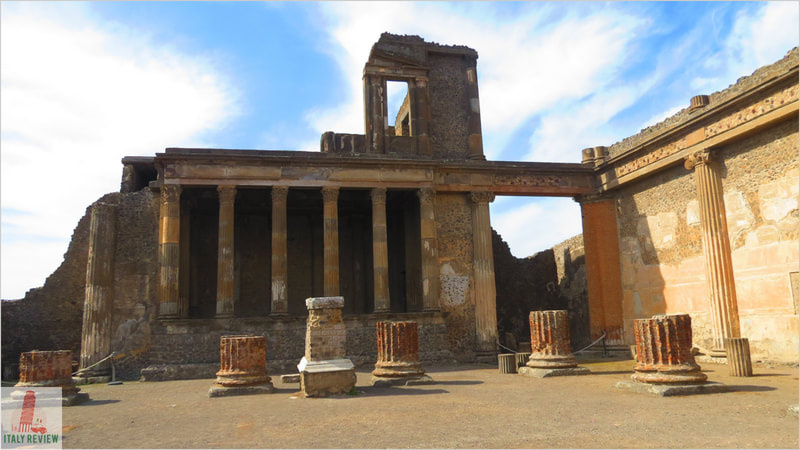
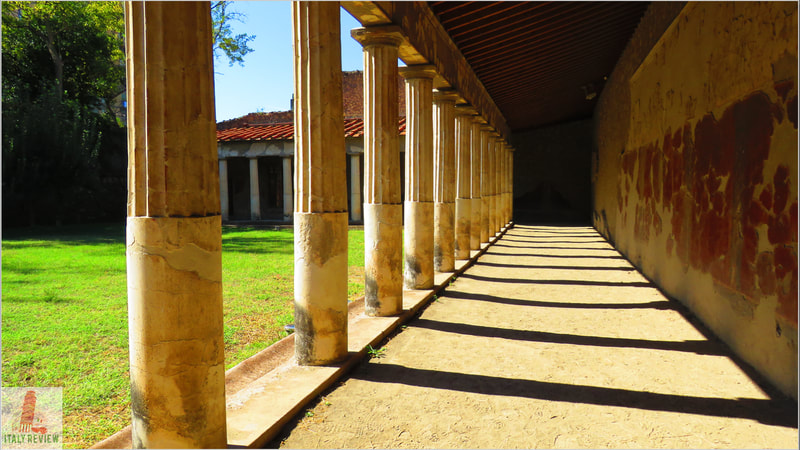
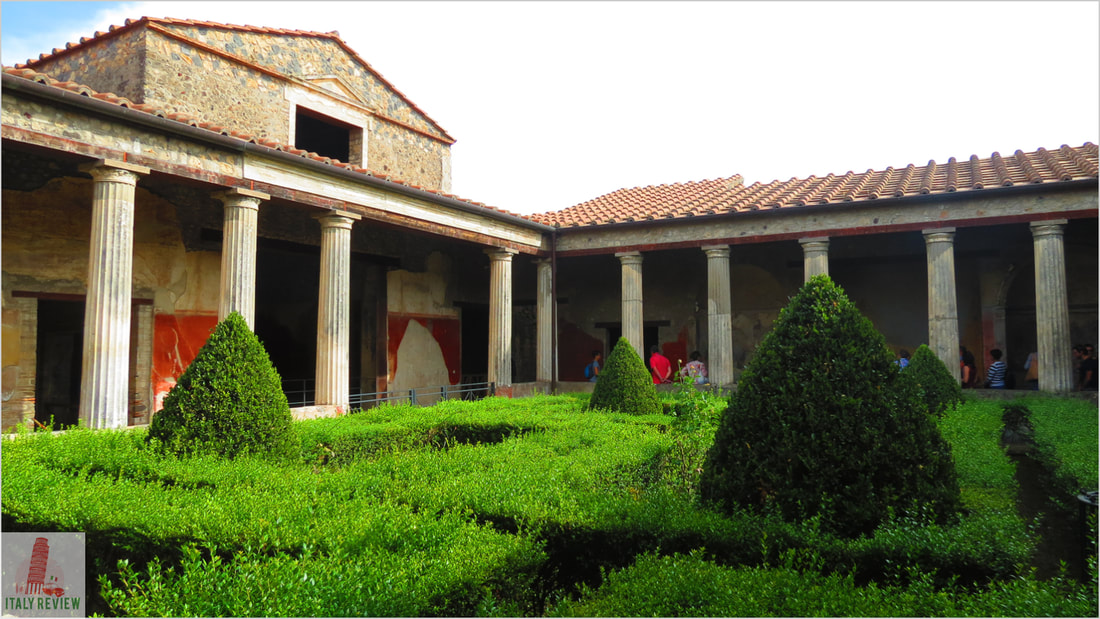
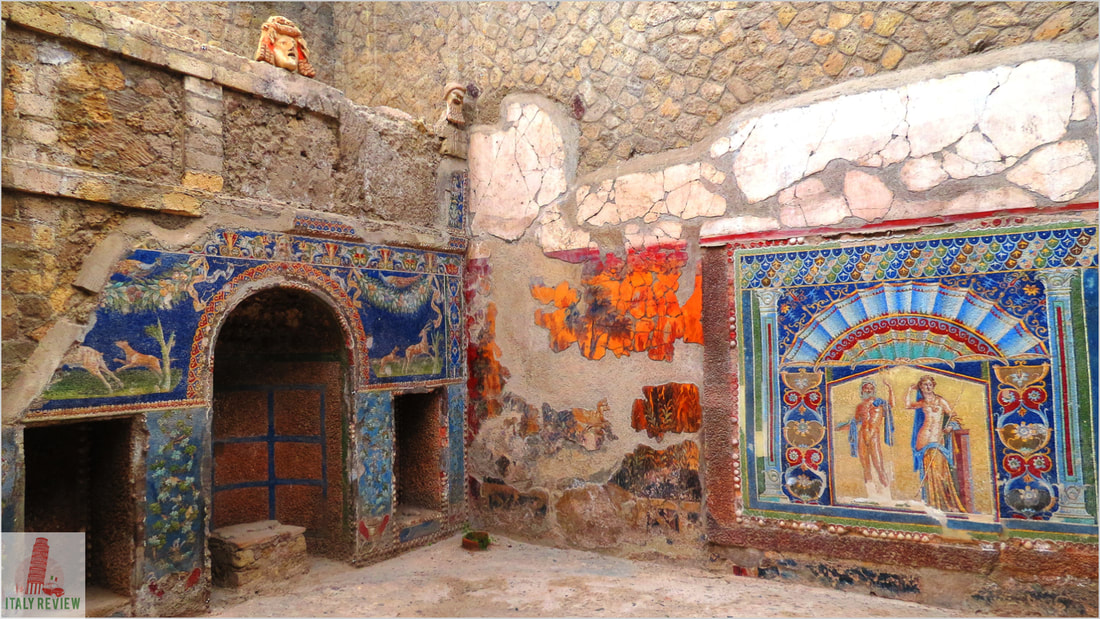
Pompei and Herculaneum were thriving Roman cities during the 1st century AD when the catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius buried them under layers of volcanic ash and debris. The volcanic ash served as a natural preservative, allowing the cities to be remarkably well-preserved, providing valuable insights into Roman urban life, architecture, and culture.
The rediscovery of these ancient cities began in the 18th century, leading to extensive excavations that uncovered well-preserved buildings, frescoes, mosaics, and artifacts, providing a unique and immersive experience of ancient Roman society.
The rediscovery of these ancient cities began in the 18th century, leading to extensive excavations that uncovered well-preserved buildings, frescoes, mosaics, and artifacts, providing a unique and immersive experience of ancient Roman society.
Key features
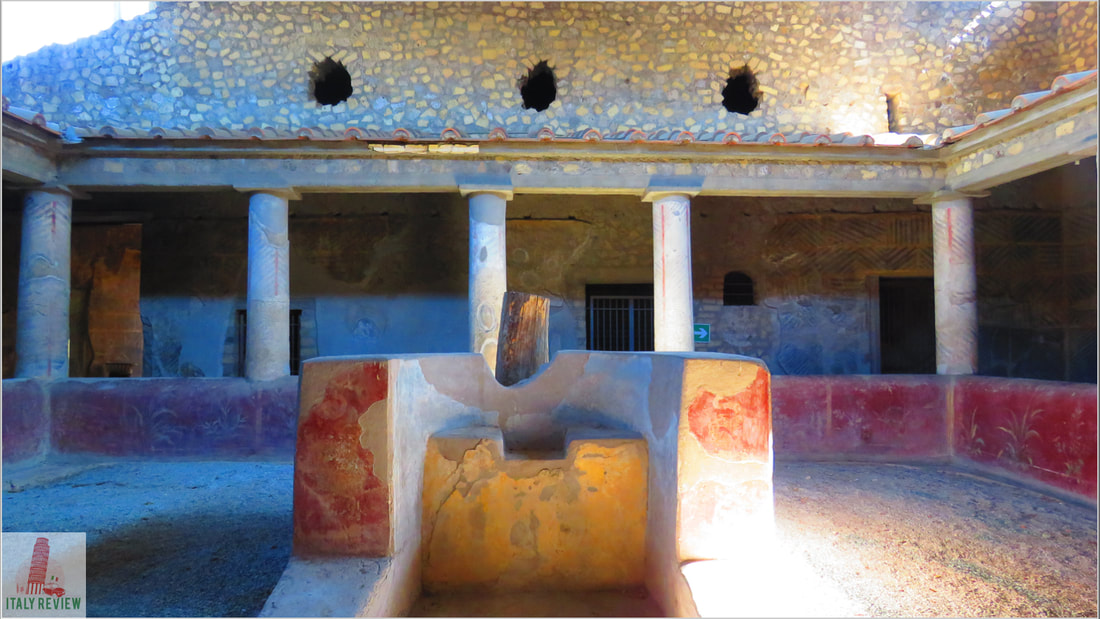
- Pompei: The ancient city of Pompei is larger than Herculaneum and features well-preserved houses, shops, temples, and the famous amphitheater. The Villa of the Mysteries, with its vivid frescoes, is one of the highlights.
- Herculaneum: Smaller than Pompei, Herculaneum's ruins include well-preserved houses, public buildings, and even wooden furniture and organic materials due to the unique conditions of the volcanic eruption.
- Villa at Torre Annunziata: The villa at Torre Annunziata, also known as Villa Oplontis, is a luxurious Roman villa that belonged to Poppaea Sabina, Emperor Nero's wife.
- Guided Tours: Guided tours are available at both Pompei and Herculaneum, offering informative insights into the history and life of the ancient Romans.
- Audio Guides: Audio guides are also available for self-guided tours, providing detailed explanations of the sites.
- Accessibility: The archaeological areas are accessible, but some areas may have uneven terrain and steps.
- Visitor Centers: Both Pompei and Herculaneum have visitor centers with facilities and information for visitors.
- Combined Tickets: Visitors can purchase combined tickets for entry to Pompei, Herculaneum, and other nearby sites.
- Transportation: The sites are well-connected by public transportation from Naples and other nearby towns.
- Conservation Efforts: The UNESCO World Heritage Site status ensures the protection and conservation of these precious archaeological treasures.
Archaeological areas of Pompei, Herculaneum and Torre Annunziata
|
Province: Metropolitan City of Naples
Region: Campania Number of sites: 3 Site types: archaeological parks Fly to: Naples International Airport |
UNESCO World Heritage Site
Archaeological areas of Pompei, Herculaneum and Torre Annunziata
Year: 1997
Archaeological areas of Pompei, Herculaneum and Torre Annunziata
Year: 1997